1.1 Why Cloud Computing?
Prior to cloud computing, modern IT world consisting of several small as well as large IT organizations used conventional methods in building IT infrastructure. But the traditional IT structure is subject to very high expenditure by the organisations for maintaining in dubious IT flow. The high cost resulted from required maintenance of a server room which include database server, mail server, firewalls, modem, switches and configurable system. A steady network of high speed internet and specialized engineers to look after the entire system were also come under the primary requirements. With day by day increase in data and need to proper
maintenance of data thus imposing a huge cost to the leading IT organisation. In order to reduce heavy pressure of IT infrastructure cost cloud computing is introduced.
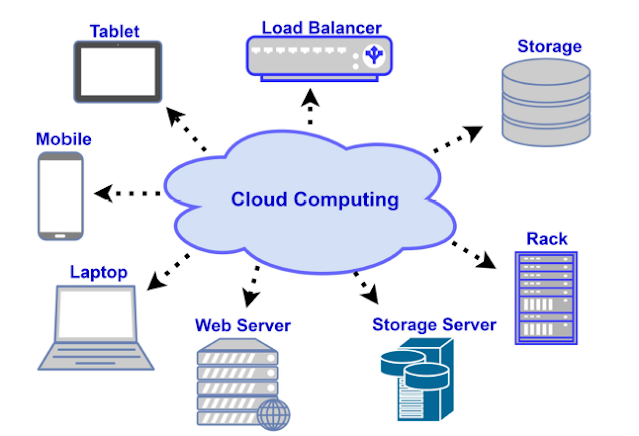 |
Figure 1.1 Cloud Computing
Cloud technology can be viewed as a metaphor for internet. Here actually a set of various hardware and software are made to work collectively in order to provide multiple services to its end users over internet. Thus a single network (typically the internet) is used to control several IT resources. Cloud computing works via internet on the basis of Pay-as-you-go pricing practice and enables the users with required IT resources. Following are the ten basic components required for enabling cloud computing, identified by IT organisations.
1. Flexibility: The system should be flexible to meet organisation’s requirements. Flexibility is also required for scaling up and down cloud capacity and providing services even to remote servers.
2. Ubiquitous access: It refers to wide accessibility of cloud service by the means of internet.
3. Automatic software updates: Software should be always up to date including security aspect.
4. Security: Important resources of users should be kept secure with cloud computing.
5. Privacy: Important resources should be delivered only to its authorized users and thus securing user’s right.
6. Reliability: Cloud enabled system should be at par or better than the existing stand-alone system.
7. Open access: The resources should be accessed easily by its users through internet.
8. Disaster recovery: Provisions of disaster recovery is crucial. Since, IT resources are distributed over different location or through multiple clouds, if one appears to be faulty processing task is automatically shifted to other redundant implementation.
9. Capital-expenditure free: The hardware requirement is reduced in cloud computing. It works through internet on the basis of ‘pay as you go’ service, thus resulted in significant cost saving for organisations.
10. Environment friendly: By increasing power effectiveness it reduces emissions of carbon contributing towards a sustainable environment condition.
1.2 History of Cloud Computing
In this section we briefly discuss about the evolution of cloud computing. There are six different phases which explain transformation of computing technology from earlier mainframe computing to modern PCs and also starting from internet and network computing to latest grid and cloud computing.
The first phase is characterized with powerful mainframes. For easy accessibility several dummy terminals were used during this phase.
Gradually mainframes were started to be replaced with more advanced PCs and these are used to serve users need in an efficient way than earlier. This constitutes the second phase in the evolution process.
In the next stage, focus was given to connect several PCs and servers by the means of local area networking in order to share computing resources.
In the fourth stage initially formed local network connectivity was expanded through interlinking one local network with others. This help to use resources those were previously remain underused and to promote applications.
The global network formed in the fourth phase became stronger when grid computing is introduced with shared memory which expanded storage capacity and additional computing power through distributed computing system.
Finally, cloud computing is emerged as an efficient means of sharing and accessing computing resources via internet.
The concept of cloud computing is thought to be pioneered by scientist John McCarthy in early 1990s. His computing views have a significant contribution in modern world of computing. He imagined computing as a public utility.
With increase in computing resources need to deliver resources to its users begin to develop. It was first started in 1969. For delivering resources these need to be connected with a network which was first introduced by J.C.R.Liclider. He developed ARPANET (Advanced Resource Project Area Network) for this purpose.
The initiatives to connect everybody in the earth with each other and also enable to access data and information from any location started from this phase.
In the process of building a virtualised world VMware was introduced in the market in 1970. VMware is software which is able to run different operating system simultaneously. The dream of commercializing computing so that it can be sold as a utility has come true through initiatives taken by different enterprises. It was begun in1999 when salesforce.com introduced web based application for delivering concerned enterprise application.
Following this, Amazon also maintains server farms to offer applications to its buyers. Amazon Web Service (AWS) app was launched in 2002. Using this app user could enjoy cloud based services like resource storage, computation and human intelligence with the help of Amazon technical wing.
After this, several medium and large scale enterprises also participated in building a global and virtual world where every people and resources can be stayed connected with each other. For example, to monitor different operating system on a single platform Xen introduced Virtual Machine Monitor (VMM), also known as hypervisor in 2003. In 2006, Amazon created Elastic Computing Cloud (EC2) services to enable small organisation and individuals who don’t have computers to rent computers for running their own applications. Big giant organisations like Google and Microsoft also launched their own web based services. The web based service of Microsoft is named as Windows Azure. To raise support for a virtualised and smarter world IBM announced Smarter Cloud framework in 2011. In 2012, oracle offered cloud services like software as a service, Platform as a service, Infrastructure as a service through oracle cloud. Soft Layer was responsible for providing cloud Infrastructure as a service from large number of data centres in the world which was taken over by IBM in 2013. With this the public cloud marked totalled up to £78 billion which is nearly 18.5% of that in 2012.
 Figure 1.2 History of Cloud Computing
AWS which was launched in 2002 become increasingly popular with the passes of time. In 2014 approximately 1.4 million servers were operated across 28 availability zones with a promise to achieve 100% renewable energy substitution. Estimates also show that global business investment for cloud infrastructure and services increases up to £108 billion, an amount 20% higher than that spent in 2012.
Not only investment but also revenue generated from this web enabled service in 2015 rose to $7.88 billion which is 69% up from the last year. With this, cloud computing opens up a new source of increasing profit for the existing IT organisations. Added to it, Morgan Stanley forecasted cloud product to constitute a significant portion (nearly 30%)in the revenue of Microsoft by 2018. Besides private cloud service, public cloud service will also increase from nearly $70 Billion to more than $141 Billion in 2019 showing an annual compound growth rate of 19.4%. It is predicted that spending on global cloud computing will reach to $241 billion in 2020.
|
1.3 Characteristics of Cloud Computing
An efficient set up of cloud computing requires some specific characteristics to be enabled by the concerned organisations. These set of characteristics are completely different from that of a
traditional web based services. For some organisation it is the cost benefit analysis associated with cloud service that is given most importance while for some other more cautions have been
given to privacy and security aspects of resources. Below, we discuss some crucial characteristics of cloud infrastructure.
1. Virtualization: A complete virtual environment is the key feature of cloud enabled services. Here there is no need to check hardware compatibility. The users need not worry at all regarding the physical state of their hardware resources.
2. Resource Pooling: Resources from different web users can be pooled together in a single networking by using cloud. Several physical and virtual resources of users can be assigned or reassigned dynamically as per consumers demand.
3. Elasticity: Availability of IT resource should be elastic in response to users demand. In a phase of rising demand resources are to make flexible enough to fulfil increasing demand while in the phase of deficient demand it should be bring back to the normal level.
4. Self service and On-demand service: It refers to the facility given to cloud users so that they can enjoy computing capabilities even when there is no interaction with cloud service providers.
5. Pricing: Use of cloud service leads to a reduced price for its users since there is in upfront cost in the beginning of contract. The users have to pay a bill amount as per their resource uses. This helps the users to keep a track of their usage and control resource cost.
6. Quality of Service: Users are provided with the best quality of services. Service providers sign a service level agreement where services are outlined with the users. This agreement helps
the users to be aware of the services.
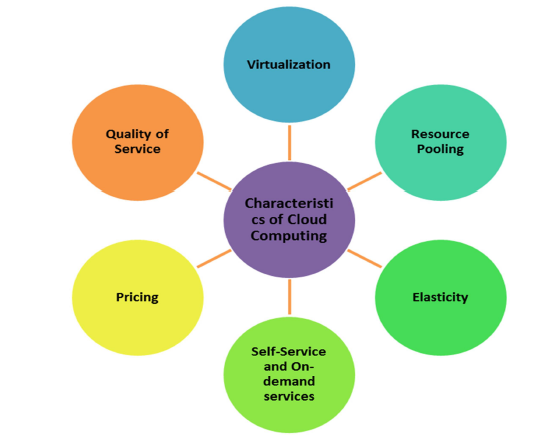
Figure 1.3 Characteristics of Cloud Computing
1.4 Benefits of Cloud Computing
According to the RightScale 2014 State of Cloud Report, 94% of the organizations surveyed are using cloud. This identifies that the uses of cloud computing has several benefits.
1. Cost efficiency: It is a cost effective technology since organisations pay only for what they use. Therefore, there is flexibility at the discretion of organisation to add to or drop cast
whenever it expands or shrink.
2. No upfront cost: Upfront cost refers to costs incurred at the beginning of any contract. In case of cloud enabled web services there is no such cost to bear. Here users can get access over
the resources in time and in their own expense of building capabilities and suitable infrastructure.
3. Fast deployment: Software based on cloud service required least time and efforts to be installed and configured.
4. Organisation focus: With easy and smooth resource management using cloud organisations can concentrate on their core business.
5. Scalable services: As per organisations requirement cloud capacity can be scaled up or down.
6. Access to remote staff: Users can get access to the remote staff by accessing cloud services. They are also allowed to share their problem on an open platform for all. This helps the organization to reach their goals.

Figure 1.4 Benefits of Cloud Computing
1.5 Risks of Cloud Computing
Despite having several benefits of cloud computing in managing IT resources, the risk associated with it cannot be ignored. The risk concerned is in the security domain of user’s resources mainly because large scale data are stored in public cloud. Followings are the risk related to cloud computing.
1. Increased security issues: Sensitive data of different organizations are stored in cloud. So, any movement of these resources require a secure access. In public cloud consumers resources are to be stored within an expanded security boundary. Overlapping security boundaries result in unauthorized access of resources by cloud providers. Both cloud users and providers follow access control norms in order to allow only authorized access to important resources.
2. Portability limitation different cloud providers: There is no fixed standard that can be determined by negotiation among all the cloud providers. As a result it becomes almost impossible for consumers to switch their resources from one provider to other.
3. Region wise legal issues: An important benefit of cloud computing is that users can access resources irrespective of their physical location. So, cloud provider build data centres in different
region for sharing consumer’s resources. But in some cases it becomes extremely important to have data centres that are under the control of definite industry or local government to satisfy privacy norms and storage policies.
4. Correct billing issues: Cloud computing offers services on pay as you go basis. Thus, consumers need to pay only for the resources they are used.
5. Loss of governance: Both consumers and providers have a shared responsibility of cloud governance. Cloud service agreement should be properly stated to the consumers. Consumers must have sufficient control over their IT resources.
REVIEW QUESTIONS
- Define cloud computing.
- What is a cloud?
- Explain the advantages and disadvantages of cloud computing.
- Why is cloud necessary?
- List of characteristics of cloud computing.
- Explain the benefits of cloud computing.
- Explain the risks of cloud computing.
- Why move to the cloud?
- What are the uses of cloud computing?
- How does cloud computing provide on-demand function.











4 Comments
E29BDE9734
ReplyDeleteinstagram organik türk takipçi
green swivel accent chair
C909F98D10
ReplyDeleteinsta takipçi
oversized swivel accent chair
5303F13A64
ReplyDeleteBeğeni Satın Al
Sahte Takipçi
Bot Takipçi Atma
614080C7A5
ReplyDeleteGörüntülü Sex
Görüntülü Show
Canlı Cam Show