What is CyberSecurity | Introduction to Advance Cyber Security:
Cyber Security:
Cyber security is the protection of internet connected system including hardware, software & program or data from cyber attacks.
Need of Cyber Security:
To protect private data
To protect intellectual data
To protect banking & financial data
To protect sensitive data
Types of Security
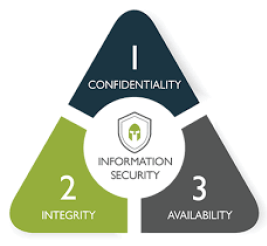
CIA Triad
The purpose of cybersecurity is to help prevent cyberattacks, data breaches and identity theft and aid in risk management.
Ethical Hacking:
Ethical hacking is the authorised & legal process of finding outvulnerabilities, threats and exploits in a system or computernetwork through penetration testing.
Types of Hackers:
Black Hat Hackers White Hat Hackers Gray Hat Hackers
Penetration Testing:
Penetration testing is an attempt to exploit the vulnerabilities to determine whether unauthorised access or other malicious activity is possible.
Types of Penetration Testing:
Network Services Web Application Wireless Social Engineering
Popular Penetration Testing Tools:
Nessus, Nmap, Metasploit, OpenSSL, Wireshark, BurpSuite, etc.
Types of Cyber Attacks:
Malware - malicious software. Piece of software written with the intent of damaging devices, stealing data. Viruses, Spyware and Ransomware are among the different kinds of malware.
Phishing - Phishing attacks are the practice of sending fraudulent communications that appear to comefrom a reputable source. It is usually done through email.
Honeytrap - Honey trapping is an investigative practice involving the use of romantic relationships for interpersonal, political or monetary purpose.
SQL Injection - It is a code injection technique that might destroy your database. SQL injection is one of the most common web hacking techniques.
Man-In-The-Middle - A man-inthe- middle (MiTM) attack is a type of cyber attack in which the attacker secretly intercepts and relays messages between two parties.
Denial-of-Service - A denial-ofservice (DoS) attack floods a server with traffic, making a website or resourceunavailable.
The Internet
Internet Protocol (IP) Address:
Internet Protocol (IP) address is an identifying number that isassociated with a specific computer or computer network. Whenconnected to the internet, the IP address allows the computers tosend and receive information. IP address serves two principal functions: host or network interface identification and location addressing.
IPv4 and IPv6:
IPv4 was the first version of IP. It was deployed for production in the ARPANET in 1983. Today it is most widely used IP version. IPv6 is the most recent version of the Internet Protocol. Internet Engineer Taskforce initiated it in early 1994.
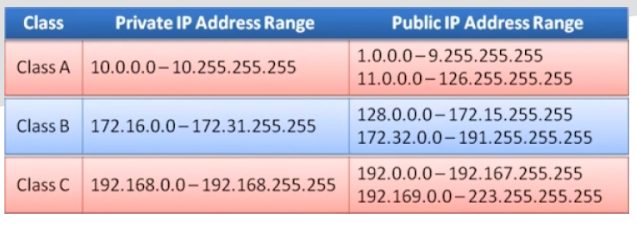
Private IP and Public IP:
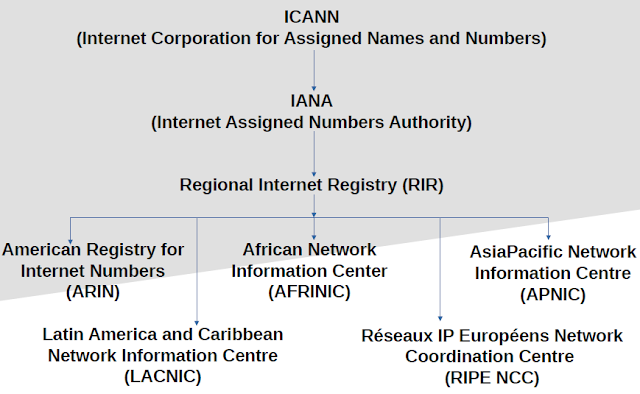
Private IP address is used with a local network and public IP address is used outside the network. Private IP address assigned by Network Administrator and Public IP address is assigned by Internet Service Provider (ISP)/ IANA. Private IP address is unique only in LAN and Public IP address unique globally.
Static IP and Dynamic IP:
Static IP Address and Dynamic IP Address both are used to identify a computer on a network or on internet. Static IP address never change and Dynamic IP address periodically change. Dynamic IP address assigned IP address dynamically to the computer by ISP. Each time computer is rebooted, ISP dynamically assigns an IP address to the device using DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol). Dynamic IP address is more secure than Static IP address.
Parts of an Email:
Phishing Email:
Identity Theft:
How to Protect:
Regularly update software & backup dataUse antivirus and firewall applicationUse complex &careful with passwordNever click on malicious linkBuild awareness about various phishing scamsAlways verify sender informationNever share the sensitive data online.
The purpose of cybersecurity is to help prevent cyberattacks, data breaches and identity theft and aid in risk management.
Ethical Hacking:
Ethical hacking is the authorised & legal process of finding out
vulnerabilities, threats and exploits in a system or computer
network through penetration testing.
Types of Hackers:
Black Hat Hackers
White Hat Hackers
Gray Hat Hackers
Penetration Testing:
Penetration testing is an attempt to exploit the vulnerabilities to determine whether unauthorised access or other malicious activity is possible.
Types of Penetration Testing:
Network Services
Web Application
Wireless
Social Engineering
Popular Penetration Testing Tools:
Nessus, Nmap, Metasploit, OpenSSL, Wireshark, Burp
Suite, etc.
Types of Cyber Attacks:
Malware - malicious software. Piece of software written with the intent of damaging devices, stealing data. Viruses, Spyware and Ransomware are among the different kinds of malware.
Phishing - Phishing attacks are the practice of sending fraudulent communications that appear to come
from a reputable source. It is usually done through email.
Honeytrap - Honey trapping is an investigative practice involving the use of romantic relationships for interpersonal, political or monetary purpose.
SQL Injection - It is a code injection technique that might destroy your database. SQL injection is one of the most common web hacking techniques.
Man-In-The-Middle - A man-inthe- middle (MiTM) attack is a type of cyber attack in which the attacker secretly intercepts and relays messages between two parties.
Denial-of-Service - A denial-ofservice (DoS) attack floods a server with traffic, making a website or resource
unavailable.
The Internet
Internet Protocol (IP) Address:
Internet Protocol (IP) address is an identifying number that is
associated with a specific computer or computer network. When
connected to the internet, the IP address allows the computers to
send and receive information.
IP address serves two principal functions: host or network interface identification and location addressing.
IPv4 and IPv6:
IPv4 was the first version of IP. It was deployed for production in the ARPANET in 1983. Today it is most widely used IP version.
IPv6 is the most recent version of the Internet Protocol. Internet Engineer Taskforce initiated it in early 1994.
Private IP and Public IP:
Private IP address is used with a local network and public IP address is used outside the network.
Private IP address assigned by Network Administrator and Public IP address is assigned by Internet Service Provider (ISP)/ IANA.
Private IP address is unique only in LAN and Public IP address unique globally.
Static IP and Dynamic IP:
Static IP Address and Dynamic IP Address both are used to identify a computer on a network or on internet.
Static IP address never change and Dynamic IP address periodically change.
Dynamic IP address assigned IP address dynamically to the computer by ISP. Each time computer is rebooted, ISP dynamically assigns an IP address to the device using DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol).
Dynamic IP address is more secure than Static IP address.
Parts of an Email:
Phishing Email:
Identity Theft:
How to Protect:
Regularly update software & backup data
Use antivirus and firewall application
Use complex &careful with password
Never click on malicious link
Build awareness about various phishing scams
Always verify sender information
Never share the sensitive data online.














0 Comments